Overview
Driver assistance technologies hold the potential to reduce traffic crashes and save thousands of lives each year. In 2023, 40,901 people died in motor vehicle crashes — many of these crashes were tied to human error. Learn more about driver assistance technologies, how they can help you, and what you should know about these technologies when buying your next vehicle.
Technology Saves Lives
Driver Assistance Technologies
Driver assistance technologies in your car not only help to keep you and your passengers safe, but also other drivers and pedestrians. When shopping for a new or used vehicle, you may notice that different manufacturers use different names for the technologies. NHTSA is helping consumers break through the confusion with explanations about how these technologies work. It’s important to understand that some driver assistance technologies are designed to warn you if you’re at risk of an impending crash, while others are designed to take action to avoid a crash. Be sure to review your vehicle’s owner’s manual for more information on your vehicle’s technology and safety features. Understanding how the technology works and how it can better protect you, your passengers and others is key.
Tech Overview
Detects a potential collision with a vehicle ahead and provides a warning to the driver.
Monitors the vehicle’s position within the driving lane and alerts the driver as the vehicle approaches or crosses lane markers.
Warns the driver of a potential collision, while in reverse, that may be outside the view of the backup camera.
Warns of a vehicle in the driver’s blind spot.

Applies brakes automatically when a forward collision is imminent. There are two types of automatic emergency braking systems that meet NHTSA’s performance specifications: dynamic brake support and crash imminent braking.
Detects a pedestrian in front of the vehicle and automatically applies brakes if a collision is imminent.
Detects a potential collision while in reverse and automatically applies brakes if a crash is imminent.
Applies brakes or provides steering if the driver begins to change to a lane where a vehicle is detected in the blind spot.

Automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to keep a pre-set distance from the vehicle in front of it.
Provides continual steering to keep the vehicle centered in its lane.
Automatically and gently steers to prevent the vehicle from departing the lane.

Automatically switches the vehicle’s headlights between low and high beams when an oncoming vehicle approaches based on lighting conditions and traffic. This is also known as semi-automatic beam switching.
Provides the driver with a clear view directly behind the vehicle when in reverse. This is also known as a rearview video system.
An automatic crash notification system notifies emergency responders that a crash has occurred and provides its location.

System provides momentary driving assistance, like warnings and alerts, or emergency safety interventions while driver remains fully engaged and attentive.
You Drive, You Monitor
You, as the driver, are responsible for driving the vehicle. All vehicle features are assistive and do not operate the vehicle. You must steer, brake, and accelerate.
Example of vehicle technologies:
- automatic emergency braking
- forward collision warning
- lane departure warning
System provides continuous assistance with either acceleration/braking OR steering, while driver remains fully engaged and attentive
You Drive, You Monitor
You, as the driver, are responsible for driving the vehicle. When engaged, the system can perform either steering OR acceleration/braking.
Example of vehicle technologies:
System provides continuous assistance with both acceleration/braking AND steering, while driver remains fully engaged and attentive.
You Drive, You Monitor
You, as the driver, are responsible for driving the vehicle. When engaged, the system can perform steering AND acceleration/braking.
Example of vehicle technologies:
- highway pilot
Level 3-5 technologies are not available on today’s vehicles for consumer purchase. Automated Vehicles for Safety has more on levels of automation.

Tech In Your Car
Technologies Explained
Forward Collision Warning
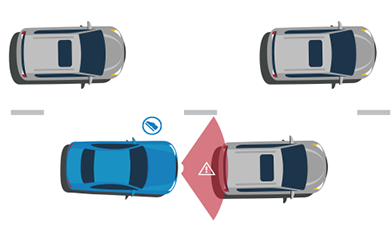
Forward collision warning systems use sensors to detect slower-moving or stationary vehicles. When the distance between vehicles becomes so short that a crash is imminent, a signal alerts the driver so that the driver can apply the brakes or take evasive action, such as steering, to prevent a potential crash. Vehicles with this technology provide drivers with an audible alert, a visual display, or other warning signals. This helps prevent frontal crashes into the rear of slower moving or stopped vehicles.
Lane Departure Warning
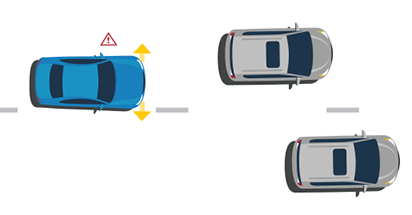
A lane departure warning system uses a camera to detect when the vehicle is veering out of its lane. An audio, visual, or other alert warns the driver of the unintentional lane shift so the driver can steer the vehicle back into its lane. This provides a valuable safety benefit and can help keep drivers and passengers safe from crashes such as when a vehicle strikes a car in an adjacent lane, including sideswiping a vehicle traveling in the same direction or hitting a vehicle traveling in the opposite direction. Also, lane departure warning could prevent incidence of road departure and subsequent crashes off roadway.
Rear Cross Traffic Warning
Blind Spot Warning
Collision Intervention
Automatic Emergency Braking
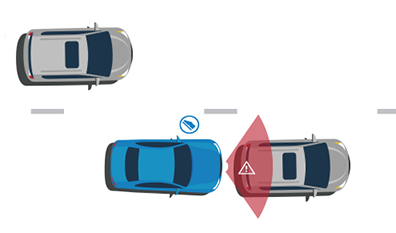
If the system detects a crash and the driver brakes, but not hard enough to avoid the crash, DBS automatically supplements the driver’s braking to avoid a crash. If the system detects a crash but the driver does not brake to at all, CIB automatically applies the vehicle’s brakes to slow or stop the car, avoiding the crash or reducing its severity.
Extensive research on this technology and on relevant performance measures showed that a number of AEB systems currently available in the marketplace are capable of avoiding or reducing the severity of rear-end crashes in certain situations.
Pedestrian Automatic Emergency Braking
Rear Automatic Braking
Blind Spot Intervention
Driving Control Assistance
Adaptive Cruise Control
Lane Centering Assistance
Lane Keeping Assistance
Other Systems
Automatic High Beams
Backup Camera
Automatic Crash Notification
NHTSA promotes the safe use and manufacture of vehicle equipment
Through safety standards and consumer information, NHTSA demonstrates its commitment to reducing crashes and saving lives in the United States. NHTSA works to inform consumers about the types of driver assistance technologies that are available and which technologies we recommend.
We now know that driver assistance technologies are the right path toward safer roads. We will work diligently to bring you updated information whenever there are breakthroughs with new driver assistance technologies.

